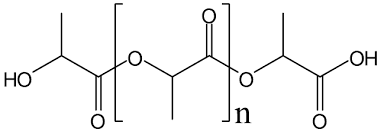
PLA or Polylactic acid is a thermoplastic monomer derived from natural resources for instance corn starch or sugarcane.moreover, meanwhile PLA can be produced from different biomass materials, it can also be mixed with other materials to provide alternative properties
PLA comes in the form of a long, narrow thread of plastic wound into a spool.
With PLA we reach no bad odor when printed, detailed prints without deformations with high hardness as well as smooth printing and it is easily recyclable Which makes PLA different from other materials. Also We have a wide range of colors among appropriate price.in conclusion,It is one of the most popular 3D printing filaments due to its low printing temperature, minimal warping, and eco-friendliness.
?WHAT IS PLA
HISTORY OF THE PLA
1932: Wallace Carothers, a chemist at DuPont, discovered polylactic acid while researching synthetic polymers. However, the technology to mass-produce it was not available.
1954: The first PLA synthesis was improved by American scientist Robert A. Wiseman, but it remained expensive.
1992: The company Cargill Dow LLC (now NatureWorks) developed an efficient industrial process to produce PLA from corn-based sugars.
Until now PLA became one of the most widely used filaments for 3D printing as the market for desktop FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers grew.
How to prepare PLA material?
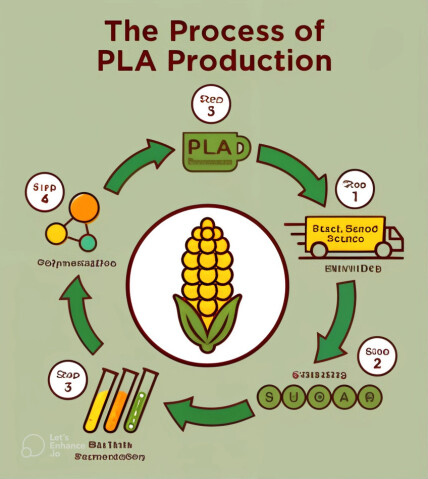
PLA is produced by fermenting carbohydrate sources such as corn starch or sugarcane under controlled conditions. Its building blocks can remain as lactic acid or lactide monomers, which are later converted into PLA, a polymer.
Initially, corn is processed through wet milling, which separates the starch particles. Then, the starch is mixed with acid or enzymes and heated. This process converts the starch into sugar (glucose) or corn syrup. Finally, the fermentation of glucose produces lactic acid, which is the primary component of PLA.
Two methods are used to produce PLA plastic from lactic acid. The first method uses lactic acid as an intermediate state, resulting in a higher molecular weight; the second involves the direct polymerization of lactic acid
Granule PLA
Ordinary PLA granules, which are composed solely of polylactic acid and are transparent, are primarily used for research purposes. These granules, when converted into filament, exhibit high brittleness and lack sufficient resistance when exposed to environmental factors and moisture. As a result, they are not particularly suitable for producing filaments for 3D printing.
Another type of granule, known as PLA+, includes additives that minimize the drawbacks of PLA filament. Its desirable properties have made it a popular choice for producing 3D printing filaments, positioning it among the top materials available. These filaments can be used for printing at low temperatures, do not require high energy, are easy to print with, and produce parts that can be utilized for a variety of applications.
TrustFil brand PLA filaments are produced in three models : Super PLA, Pro PLA and Eco PLA in a variety of colors. Our PLA filaments rank among the best products available on the market in terms of quality, cost, uniqueness, and high-precision printing.



Ultimately, PLA is an excellent and appealing material for 3D printing. It is highly versatile and easy to work with, available in a wide range of qualities and compositions. It is simple and cost-effective to use, making it the best material for visual prototyping.



PLA materials are derived from the environment and are bio-based, meaning they are plant-based biodegradable plastics. Additionally, PLA is a thermoplastic, which means it can be melted and reshaped without losing its mechanical properties, making it mechanically recyclable.
Why PLA?
In 3D printing, PLA is highly popular due to its printability and adaptability. Additionally, PLA applications include surgical sutures and implants, as it can regulate lactic acid in the body without adverse effects. PLA is also used in the production of disposable items (such as spoons and forks), household appliances, hygiene products, and even diapers. Overall, it is recognized as a safe and healthy plastic.
Applications of PLA?
Printing and Performance
The printing temperature for PLA filament can range between 178°C and 240°C. If the PLA filament is of higher quality, often due to the purity of the resin and lack of contamination, it can be printed at a lower temperature. However, it’s worth noting that the printing temperature is also influenced by the filament’s color. The optimal printing temperature will also depend on your printing environment. If the printing temperature is too high, you may notice that the extruder leaks PLA while moving, leaving thinner plastic trails between different areas of the print. If this happens, lower the printing temperature until the extruder no longer leaks PLA. On the other hand, if the printing temperature is too low, the PLA layers may not adhere properly to each other, potentially resulting in a rough surface or weak areas that easily separate. 3D printing with PLA filament should be done at a speed between 30 mm/s and 90 mm/s, though keep in mind that this range can vary depending on your specific filament and printer.
Conclusion